Arrhythmia
East Cardiovascular Specialists offers numerous in-office diagnostic
procedures to diagnose heart rates that are too fast, too slow or irregular as well as symptomatic patients experiencing palpitations, dizziness or passing out. Dr East utilizes evidence-based medical approaches for the management of his patients.
Overview
East Cardiovascular Specialists offers a host of an office diagnostic procedures…
Heart rhythm problems (heart arrhythmias) occur when the electrical impulses that coordinate your heartbeats don’t work properly, causing your heart to beat too fast, too slow or irregularly.
Heart arrhythmias (uh-RITH-me-uhs) may feel like a fluttering or racing heart and may be harmless. However, some heart arrhythmias may cause bothersome — sometimes even life-threatening — signs and symptoms. arrhythmias are often made worse — or are even caused — by a weak or damaged heart, you may be able to reduce your arrhythmia risk by adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle.
What’s a normal heartbeat?
Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). Your heart rhythm is normally controlled by a natural pacemaker (sinus node) located in the right atrium. The sinus node produces electrical impulses that normally start each heartbeat. These impulses cause the atria muscles to contract and pump blood into the ventricles.
The electrical impulses then arrive at a cluster of cells called the atrioventricular (AV) node. The AV node slows down the electrical signal before sending it to the ventricles. This slight delay allows the ventricles to fill with blood. When electrical impulses reach the muscles of the ventricles, they contract, causing them to pump blood either to the lungs or to the rest of the body.
In a healthy heart, this process usually goes smoothly, resulting in a normal resting heart rate of 60 to 100 beats a minute.
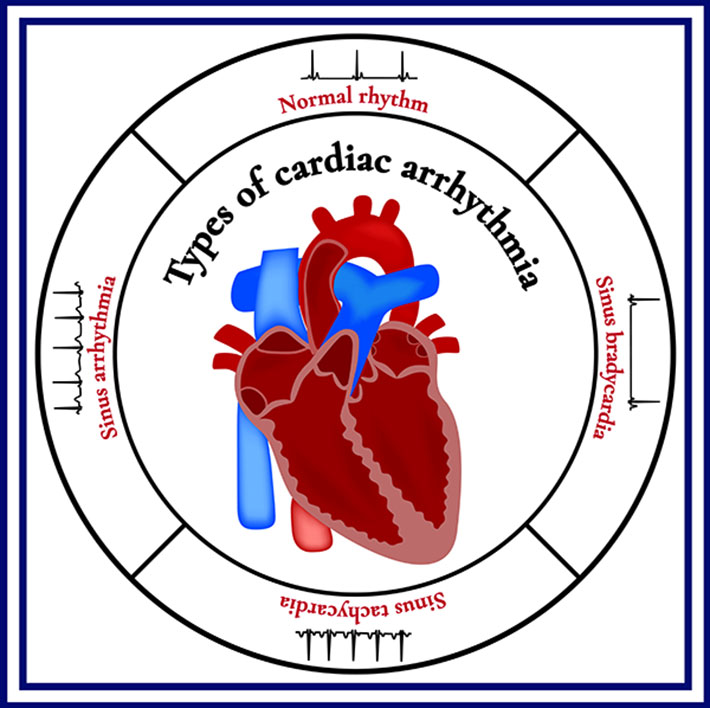
Types of arrhythmias.
Doctors classify arrhythmias not only by where they originate (atria or ventricles) but also by the speed of heart rate they cause:
Tachycardia (tak-ih-KAHR-dee-uh). This refers to a fast heartbeat — a resting heart rate greater than 100 beats a minute.
Bradycardia (brad-e-KAHR-dee-uh). This refers to a slow heartbeat — a resting heart rate less than 60 beats a minute.
Not all tachycardias or bradycardias mean you have heart disease. For example, during exercise it’s normal to develop a fast heartbeat as the heart speeds up to provide your tissues with more oxygen-rich blood. During sleep or times of deep relaxation, it’s not unusual for the heartbeat to be slower.
Symptoms
Arrhythmias may not cause any signs or symptoms. In fact, your doctor might find you have an arrhythmia before you do, during a routine examination. Noticeable signs and symptoms don’t necessarily mean you have a serious problem, however.
Noticeable arrhythmia symptoms may include:
• A fluttering in your chest
• A racing heartbeat (tachycardia)
• A slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
• Chest pain
• Shortness of breath
Other symptoms may include:
• Anxiety
• Fatigue
• Lightheadedness or dizziness
• Sweating
• Fainting (Syncope) or near fainting.